Sample Geometries
The features described in this topic are only available if you are licensed to use Leapfrog EDGE with Leapfrog Geo.
This topic describes the declustering object available in the Sample Geometry folder. It is divided into:
- Creating a New Declustering Object
- The Declustering Object in the Project Tree
- Applying a Declustering Object
The declustering object is a tool for calculating local sample density. It can be used to provide confidence in an estimate, a value for determining boundaries, or a declustering weight that can be used to remove sampling bias from a set of values. Common traditional techniques for declustering utilise a grid or polygonal cells.
In Leapfrog Geo, the declustering object is used to calculate declustering weights that are inversely proportional to the data density at each sample point. A declustering object can be used by an inverse distance estimator.
Creating a New Declustering Object
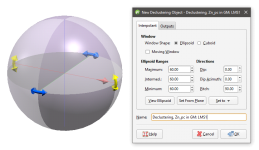
To create a new declustering object, right-click on the Sample Geometry folder and select New Declustering Object. The New Declustering Object window will appear and an ellipsoid will be added to the scene:
The ellipsoid has two sets of handles; click on the ellipsoid to toggle between them. The red, green and blue set is for setting the Ellipsoid Ranges when dragging the outer arrows, and repositioning the widget along the scene axes when dragging the inner arrows. The yellow, blue and red set (shown above) is for setting the Directions.
General Settings
The General tab of the New Declustering Object window is in three parts, Window, Ellipsoid Ranges and Directions.
The Window section defines the declustering object’s shape:
- The Window Shape can be Ellipsoid or Cuboid. Select Cuboid to approximate traditional grid declustering. The Ellipsoid option avoids increased density values for sampling oriented away from axes.
- The Moving Window option acts similarly to a rolling average by moving the window incrementally in overlapping steps, providing a much smoother result.
- Disabling Moving Window approximates a traditional grid behaviour; a single fixed window is used around each evaluation location and the density is simply the count of all input points within the window.
- Enabling Moving Window implicitly averages the point count over all possible windows that contain the evaluation location.
The Ellipsoid Ranges settings provide the same anisotropy controls used elsewhere in Leapfrog Geo, determining the relative shape and strength of the ellipsoid in the scene. Including them here provides additional advantages over traditional grid declustering.
- The Maximum value is the range in the direction of the major axis of the ellipsoid.
- The Intermed. value is the range in the direction of the semi-major axis of the ellipsoid.
- The Minimum value is the range in the direction of the minor axis of the ellipsoid.
The ellipsoid’s outer red, green and blue handles adjust the Ellipsoid Ranges.
The Directions settings determine the orientation of the ellipsoid in the scene, where:
- Dip and Dip Azimuth set the orientation of the plane for the major and semi-major axes of the ellipsoid. Dip is the angle off the horizontal of the plane, and Dip Azimuth is the compass direction of the dip.
- Pitch is the angle of the ellipsoid’s major axis on the plane defined by the Dip and Dip Azimuth. When Pitch is 0, the major axis is perpendicular to the Dip Azimuth. As Pitch increases, the major axis points further down the plane towards the Dip Azimuth.
The ellipsoid’s yellow, blue and red handles adjust the Directions.
The moving plane can also be useful in setting the anisotropy Directions. Add the Moving Plane to the scene, and adjust it using its controls. Then click the Set From Plane button to populate the Dip, Dip Azimuth, and Pitch settings.
You can also use the Set to list to choose different from the variogram models available in the project.
To approximate grid declustering, set the Window Shape to Cuboid, disable the Moving Window and set the Maximum, Intermed. and Minimum ranges to be equal values.
Outputs
The Outputs tab of the New Declustering Object window features Attributes to calculate. Value and Status will always be calculated, but you can optionally include NS (number of samples), MinD (distance to closest sample) or AvgD (average distance to sample).
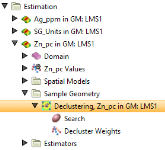
The Declustering Object in the Project Tree
Enter a name for the declustering object and click OK to create it. It will be added to the project tree in the Sample Geometry folder. Expand it to see its parts, which can be individually added to the scene:
Double-click on the declustering object in the tree to edit it.
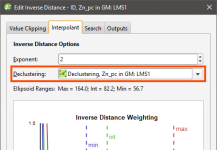
Applying a Declustering Object
Leapfrog Geo supports declustering in the inverse distance estimator. To decluster data, select a declustering object from the Declustering dropdown list:
When no declustering object is selected, the inverse distance estimator is the standard inverse distance weighted method.
Got a question? Visit the My Leapfrog forums at https://forum.leapfrog3d.com/c/open-forum or technical support at http://www.leapfrog3d.com/contact/support