Directional Pass/Reject (DPAS)
Use the Directional Pass/Reject option to apply a directional pass/reject filter.
Directional Pass/Reject Filter dialog options
|
Starting cut-off azimuth) |
The low cut-off angle in degrees azimuth, in space domain (geological strike). Note that this angle is 90 degree different from the k0 (see figure below) in frequency domain. ( = k0-90.0) |
|
Ending cut-off azimuth) |
The high cut-off angle in degrees azimuth, in space domain (geological strike). Note that this angle is 90 degree different from the k1 (see figure below) in frequency domain. ( = k1-90.0) |
|
|
Select "Pass" or "Reject" (Default is to pass the band). |
Application Notes
Directional pass/reject filter
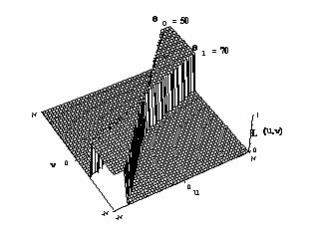
Parameters:
|
k0 |
the low cut-off angle in degrees azimuth (from North). |
|
k1 |
the high cut-off angle in degrees azimuth (from North). |
|
0/1 if 1, pass the defined band; if 0, reject the defined band. The default is to pass the band. |
As with the bandpass filter, the directional-pass often suffers from Gibb's Phenomena ringing because the spectrum is cut so abruptly. We recommend using the directional cosine filter (DCOS) instead.
Wavenumber domain variable definition
|
k |
Wavenumber domain increment, used to depict a radially symmetrical variable. |
where: np is the number of points cs is the cell size |
|
u |
X component in the wavenumber domain. | k = 2π ( i μ+j ν ) |
|
v |
Y component in the wavenumber domain. |
|
|
r |
Radial component in the wavenumber domain. |
|
|
θ |
Polar component in the wavenumber domain. |
|
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support
© 2023 Seequent, The Bentley Subsurface Company
Privacy | Terms of Use

 Pass
Pass Reject
Reject