Array Base Properties
In the database window, use the right-click menu option Array Base Properties to populate or edit the increment base property of a sensor data array channel.
Array Base Properties dialog options
|
Base
|
Depending on the type of geophysical data, the array increments may be time, distance or velocity. Select the appropriate type, or a type that fits your processing goal. Doing so will refresh the top most entry label, indicating the array size. The options are:
|
|
Units |
Specifying the units is optional. The units drop-down list is populated in context with the Base specified. |
|
Initial value | Delay time | Base frequency |
The label of this entry is contextually set and depends on the nature of the Base parameter. The first element of the array may not be at zero. The Initial value, Delay time, Base frequency define the gap to the first element of the array. This attribute is stored in the data array header. |
|
Time windows | Increment | Frequencies |
The label is contextually set relative to the above parameter. You can enter the property increments in a few different ways. Time windows is a special case generally used in IP. In this instance, both the intervals and the cumulative time are displayed. The increment parameter allows you to define the increments of the selected base property. The vertical axis of the Depth attribute increases downwards, while the vertical axis of the Elevation attribute increases upwards. Although you are not prevented from defining the Depth attribute with a negative increment, you are discouraged from doing so because this combination is equivalent to defining the Elevation attribute with a positive increment. |
|
[Copy from...] |
This button will appear only if there is at least one other array channel of an equal dimension that carries a base property. If there is only one other such array, the name of the array will be shown on the button, otherwise clicking the button will pop up a list of arrays with on-board properties to choose from. |
|
[Import from database] |
Click this option if you have the property information in a database and the dialog Import Time Windows from Database will appear to prompt you for the required information. |
|
[Export to database] |
Click this option to save the property information as currently displayed to a database for later use. You will be prompted for the output database name. |
|
Index offset |
If the window database has more elements than the current array channel in focus, you may need to offset the 1st element of the array in focus and assign a later time to it. |
|
Show hidden windows |
Array elements for which no data has been supplied will not be displayed initially. If you would like to see these elements check this box. |
Application Notes
The intent of this tool is to concatenate the size of the database, when the data array increment of a channel is the same throughout the database. This information is stored in and extracted from the channel header. A number of Oasis montaj extension tools require the array property information in order to proceed. This tool allows you to set the property, export, and import it.
The table at the end of the dialog shows the number of increments and their Start, Middle, End, and Width values.
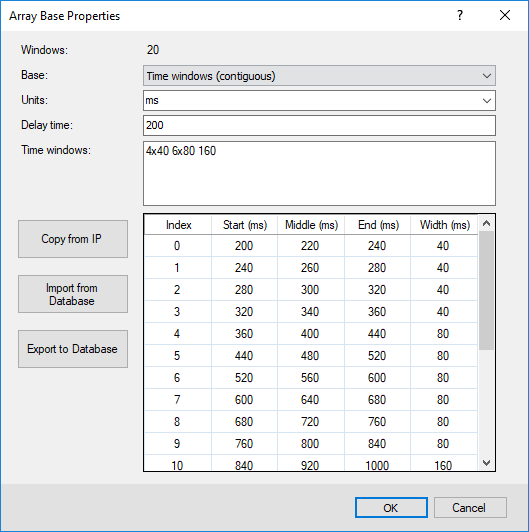
Figure 1: Contiguous time windows. Time increments are provided as a set of consecutive time windows
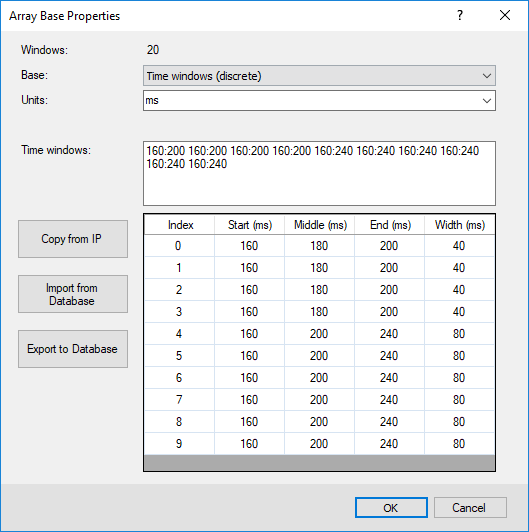
Figure 2: Discrete time windows. Time gates are provided as a set of potentially overlapping start & end times.
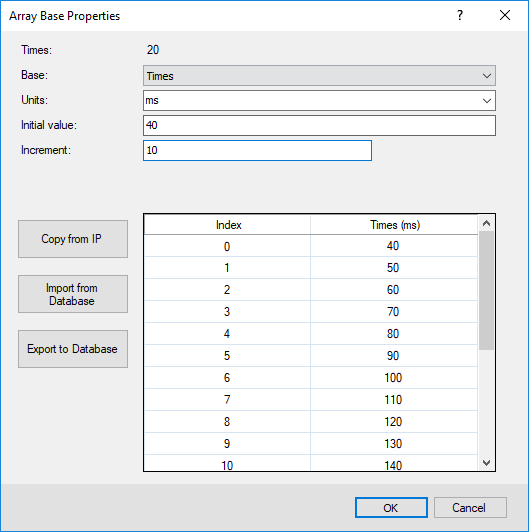
Figure 3: The widths can also be constants.
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support
© 2023 Seequent, The Bentley Subsurface Company
Privacy | Terms of Use
