7x7 and 9x9 Symmetric Convolution Filters
Use the 7x7 Symmetric Convolution or the 9x9 Symmetric Convolution option (GRIDFLTn GX), from the Grid and Image > Filters menu, to apply a nxn (n = 7 or 9 ) symmetric filter to a grid using any number of passes.
7x7 Symmetric Convolution / 9x9 Symmetric Convolution dialog options
|
File name of the input grid (.grd file). Script Parameter: GRIDFLTN.GRD |
|
|
New resultant grid |
File name of the new grid (.grd file). Script Parameter: GRIDFLTN.NEWn (n=7 or 9) |
|
OPTION 1 - Select a predefined filter |
Name of predefined nxn symmetric filter (option 1 of 3):
Script Parameter: GRIDFLTN.DEFFILTn (n=7 or 9) [0: User Definition, 1: Least Square, 2: Laplacian of Gaussian] |
|
OPTION 2 - Choose a filter file |
Name of file containing the nxn symmetric filter (option 2 of 3). Script Parameter: GRIDFLTN.FILTn (n=7 or 9) |
|
OPTION 3 - Type coef. filter string |
Coefficient of filter string - six, ten or fifteen comma-delimited numbers for 5x5, 7x7 and 9x9 filters, respectively, e.g., 1,2,3,4,5,6 etc.,(option 3 of 3). Script Parameter: GRIDFLTN.FILTSTRn (n=7 or 9) |
|
Number of passes to apply |
Number of filter passes to apply to create the new grid. Script Parameter: GRIDFLTN.PASSn (n=7 or 9) |
Application Notes
The nxn symmetric filter consists of an nxn convolution symmetric matrix. These types of filters are used commonly in image processing applications.
There are three options to choose from for defining the filter you wish to use:
- You can enter the name of a predefined filter in the .DEFFILTn parameter.
- Enter into the .FILTn parameter, the name of a filter file you have created.
- Define your own filter: enter the coefficients of the filter as a command delimited string into the .FILTSTRn parameter.
A filter file contains the 6, 10 or 15 filter coefficients starting with the centre point of the centre row for 5X5, 7X7 and 9X9 respectively, then continued with successive rows listed centre then the next right, then continued with successive rows listed centre to right:
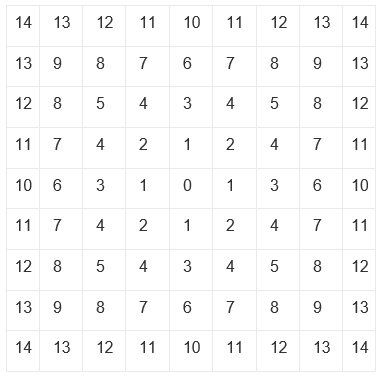
For example, in this 7x7 symmetric filter, set filter values for 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 in the filter file in this order. There cannot be any spaces within or between numbers, and the numbers themselves must be real numbers in the range of-1e31 to 1e32.
If you enter the 6, 10 or 15 coefficients as a string, then enter them just like the above filter file format, using commas to delimit the values.
If there are any grid dummies within filter coverage (i.e. 7x7 area), they will be replaced by interpolated values, except for the centre value if it is a dummy. The resultant grid will have the same coverage as the input grid.
Some standard filters are provided with the installation:
- The Least Square filter is a smoothing filter that minimizes the variance in the data.
- The Savitzky-Golay filter removes the background chatter from the data.
- The Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter helps highlight regions of rapid intensity change. Therefore, it is often used for edge detection. The Laplacian filter (
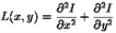 ) would generally produce a noisy outcome, so it is convolved with a Gaussian smoothing filter to yield the Laplacian of Gaussian:
) would generally produce a noisy outcome, so it is convolved with a Gaussian smoothing filter to yield the Laplacian of Gaussian:
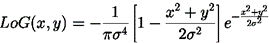
Where σ = 1.4
For further details see Spatial Filters - Laplacian/Laplacian of Gaussian (dmu.ac.uk)
To position the edges of the anomalies at the vicinity of 0, the filter should be applied to a grid with a mean of 0. Since the central values of the LoG filter are large negative values compared to the input grid, the high/low regions will be flipped on output. If you would like to maintain the sign correlation between the inputs and output grids, you could either multiply the output grid by -1 or save and use a custom filter in which all the LoG coefficients are multiplied by -1 .
- The Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter helps highlight regions of rapid intensity change. Therefore, it is often used for edge detection. The Laplacian filter (
|
Leastsqu.5x5 |
Least Square smoothing filter. |
|
SavitzkyGolay.5x5 |
Symmetrical Savitzky-Golay noise filter of power 4. |
|
Laplacian.9x9 |
Symmetrical Laplacian of Gaussian filter. |
You can find numerous filters online that would enhance or attenuate certain signals in the data; for example, the 5x5 Unsharp Masking filter smooths out point to point noise: 476, -24, -16,-6,-4,-1.
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support
© 2023 Seequent, The Bentley Subsurface Company
Privacy | Terms of Use
