Apparent Susceptibility Calculation (SUSC)
Use the Apparent Susceptibility Calculation option to apply the apparent susceptibility calculation filter.
Apparent Susceptibility Calculation dialog options
Application Notes
Apparent Susceptibility Calculation
A susceptibility filter is a compound filter that performs a reduction to the pole, downward continuation to the source depth, correction for the geometric effect and division by the total magnetic field to yield susceptibility. Apparent susceptibility mapping assumes a simple geometric model. The response is assumed to be caused by a collection of vertical, square-ended prisms of infinite depth extent, the horizontal dimensions of which are equal to the input grid cell size. This is an idealized approximation hence the descriptor Apparent.
Where:
|
I |
Geomagnetic inclination in ° |
|
D |
Geomagnetic declination in ° azimuth |
|
h |
Depth in ground units, relative to the observation level |
|
Ia |
Inclination for amplitude correction (never less than I) Default is ± 20 degrees. If |Ia| is specified to be less than |I|, it is set to I. |
|
a |
½ Cell size |
Wavenumber domain variable definition:
|
k |
Wavenumber domain increment, used to depict a radially symmetrical variable. |
where: np is the number of points cs is the cell size |
|
u |
X component in the wavenumber domain. | k = 2π ( i μ+j ν ) |
|
v |
Y component in the wavenumber domain. |
|
|
r |
Radial component in the wavenumber domain. |
|
|
θ |
Polar component in the wavenumber domain. |
|
Ground_unit is the survey ground units as defined in your grid (e.g., metre or feet). Ground units may be left undefined. Note that the elevation of a gridded mag data is a constant (or close approximation).
The susceptibility filter operator calculates the apparent magnetic susceptibility of the magnetic sources using the following assumptions:
-
The IGRF has been subtracted from the input magnetic field prior to filtering.
-
There is no remanent magnetization.
-
All magnetic response is caused by a collection of vertical, square-ended prisms of infinite depth extent.
-
The resulting susceptibility data is dimensionless (cgs units).
The validity of the results is naturally subject to how well the actual observed field conforms to these assumptions.
To calculate the IGRF parameters, the date and geographic location are needed. If this information is not already supplied, you will be prompted to define it. The IGRF field strength is only required for apparent susceptibility calculation, but is re-calculated along with the inclination and declination in the other controls, so the values are always synchronized.
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support
© 2024 Seequent, The Bentley Subsurface Company
Privacy | Terms of Use

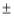 20.
20.