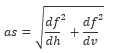Analytic Signal
Use the 1D FFT > Analytic Signal menu option (FFTAS GX) to calculate the analytic signal of a potential field (magnetic or gravity) profile.
Strictly, the FFTAS GX produces the amplitude of the analytic signal; however, for the sake of brevity and consistent with conventional usage, we simply refer to it here as the analytic signal.
FFT Analytic Signal dialog options
|
Channel to process |
Select the input channel. Script Parameter: FFTAS.IN |
|
Output analytic signal channel |
Specify the output analytic signal channel. Script Parameter: FFTAS.OUT |
|
[Set Sampling] |
Click the button to open the Set FFT Sampling Parameters dialog to set the channel data sampling parameters and ensure that the input data is appropriately sampled for 1D FFT. |
Application Notes
To generate the analytic signal, the database must contain X & Y channels.
By default, the analytic signal of potential field profile data is calculated in units of profile_units/distance_increment. However, this may not be the desirable outcome. To yield units/m, set the sampling interval to 1 meter.
The analytic signal is sensitive to regional gradients in the data and to overlapping anomalies. Gradients and long wavelengths in the data that are not of interest should be removed from profiles before calculating the analytic signal. Use the Polynomial option (found on the Database Tools > Filters menu) to remove a trend from the data. Apply a high-pass filter (Butterworth or Gaussian) to remove long wavelengths. You might also consider calculating the analytic signal from the vertical derivative to help resolve overlapping anomalies.
Analytic Signal
The analytic signal (as) of a profile is defined as:
Where:
is the horizontal derivative of the profile data along the survey path.
is the vertical derivative of the profile data.
See Also:
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support
Copyright (c) 2025 Bentley Systems, Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Privacy | Terms of Use