Importing a Map or Image
This topic describes how to import an image or map into the GIS Data, Maps and Photos folder. If you wish to import a cross section image into Leapfrog Works, import it into the Cross Sections and Contours folder using the New Cross Section From Image option. See Importing Cross Sections for more information.
Image formats Leapfrog Works supports include:
- PNG Files (*.png)
- JPEG Files (*.jpg, *.jpeg)
- TIFF and GeoTIFF Files (*.tiff, *.tif)
- Windows Bitmap Files (*.bmp)
- Graphics Interchange Format Files (*.gif)
To import an image in one of these formats, right-click on the GIS Data, Maps and Photos folder and select Import Map. Navigate to the folder that contains the image file and select it. You can select multiple files using the Shift and Ctrl keys.
Click Open to import the file or files.
- If you are importing a single file and it does not contain georeference data, the Import Map window will be opened in which you can add georeferencing information. See Manually Georeferencing Images below.
- If you are importing a single file that contains georeference data, it will automatically be added to the GIS Data, Maps and Photos folder.
- If you are importing multiple files, all files will automatically be added to the GIS Data, Maps and Photos folder, even those that do not contain georeferencing information.
If you display an image in the scene and nothing is visible, it may be that it does not contain georeference data and was imported along with other image files. Double-click on the image in the project tree to add the georeference information, as described in Manually Georeferencing Images below.
The rest of this topic describes how to georeference, crop and export images. It is divided into:
Manually Georeferencing Images
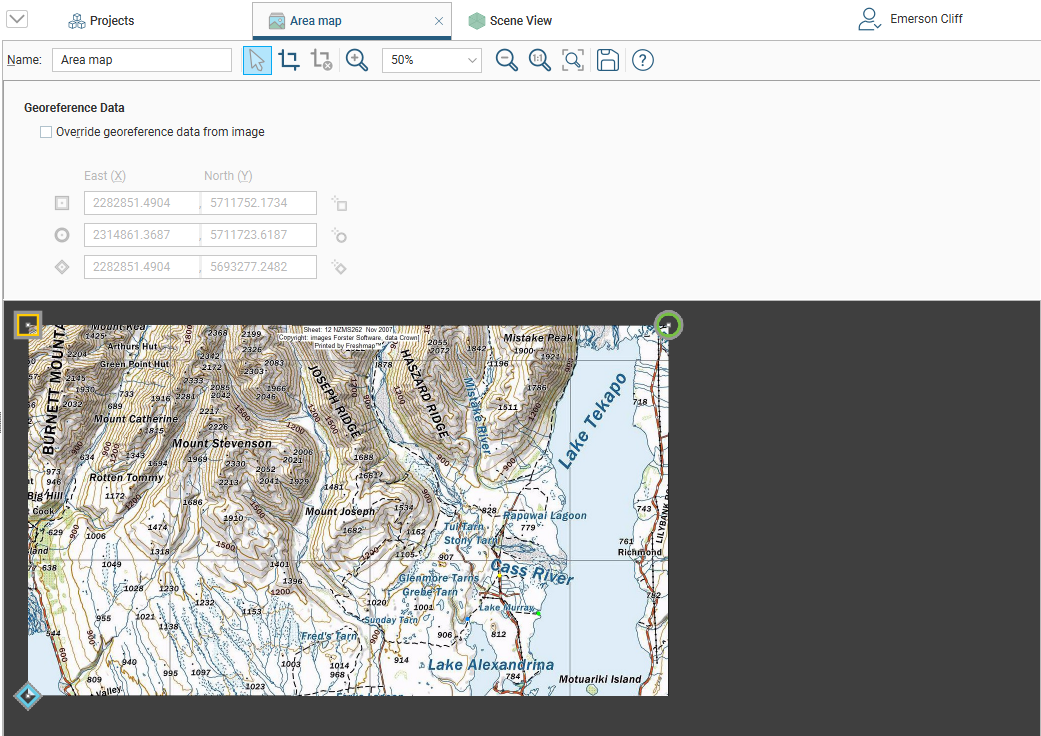
In Leapfrog Works, three markers (![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ) are used to display the georeference data for imported images. You can see these markers in the scene when you double-click on an imported image, which opens a tab that has tools for cropping the image and editing its georeference data:
) are used to display the georeference data for imported images. You can see these markers in the scene when you double-click on an imported image, which opens a tab that has tools for cropping the image and editing its georeference data:
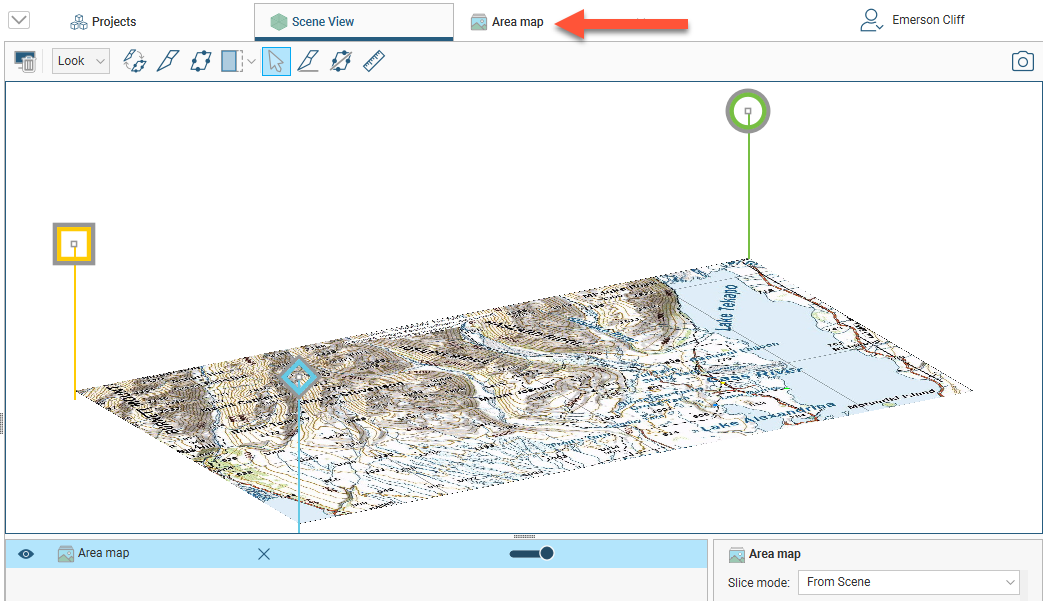
When you switch back to the scene, you can see the georeferencing markers:
When an image does not contain georeference data, or if a georeferenced image has coordinates that are not correct, you will need to georeference the image manually using the three reference markers (![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ). If the image already has georeference information that is not correct, tick the Override georeference data from image box.
). If the image already has georeference information that is not correct, tick the Override georeference data from image box.
Click on a marker button, then move it to the required location on the image using the mouse or the arrow keys. Once each marker is correctly positioned, enter the real-world X and Y coordinates for each marker:
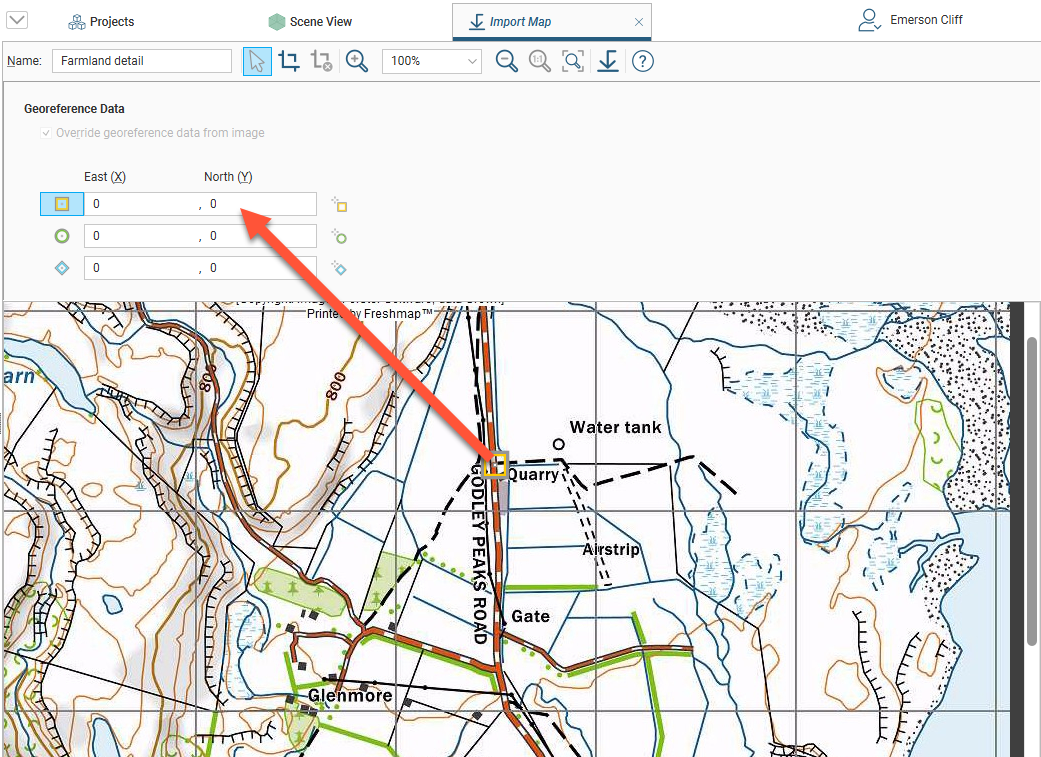
There are two ways to do this:
- Enter the coordinates for each marker in the East (X) and North (Y) fields. As you enter the coordinates, the positions of the markers will be displayed in the scene.
- Copy coordinates from the scene using the three scene markers (
 ,
,  ,
,  ).
).
The second method is useful when you already have other objects correctly georeferenced in the project. For example, if you have another map or some polylines or points in the project and wish to import a map that aligns perfectly, you can reference the imported image directly against the existing project data.
Tear off the dockable image tab so it floats over the scene view and move it so you can see enough of the scene to work in both windows. Once you have positioned your points, click the Save button rather than closing the image window so you will be able to preview the results and make adjustments as needed.
To manually georeference the imported image using the three scene markers:
- In the image tab, position the marker (
 ,
,  ,
,  ) on the image being imported.
) on the image being imported. - Click the corresponding copy coordinates marker (
 ,
,  ,
,  ).
). - Click in the scene the point corresponding to where in the image the marker was placed.
The coordinates in the scene will be entered into the image tab.
If the alignment is not perfect, make adjustments to improve the match. There are two ways to make these adjustments:
- In the scene window, zoom in to the point where you wish to place a copy-coordinates marker (
 ,
,  ,
,  ), click the marker in the image tab, then click the point in the scene zoomed in, or
), click the marker in the image tab, then click the point in the scene zoomed in, or - In the image tab, zoom in to the point where the reference marker has been positioned and adjust the location.
Click the Save button to preview the change before closing the image tab.
Cropping Images
Images larger than 16384 by 16384 pixels will be scaled down. Reducing your images in size below this limit will avoid scaling. You can scale down images in an external image editor, or you can crop imported images in Leapfrog Works.
Cropping an image to only the area of interest will reduce video RAM usage and may improve graphics performance. To crop an image, double-click on the image in the project tree. In the window that appears, select the Crop Image button (![]() ) and then drag around the part of the image you wish to use.
) and then drag around the part of the image you wish to use.
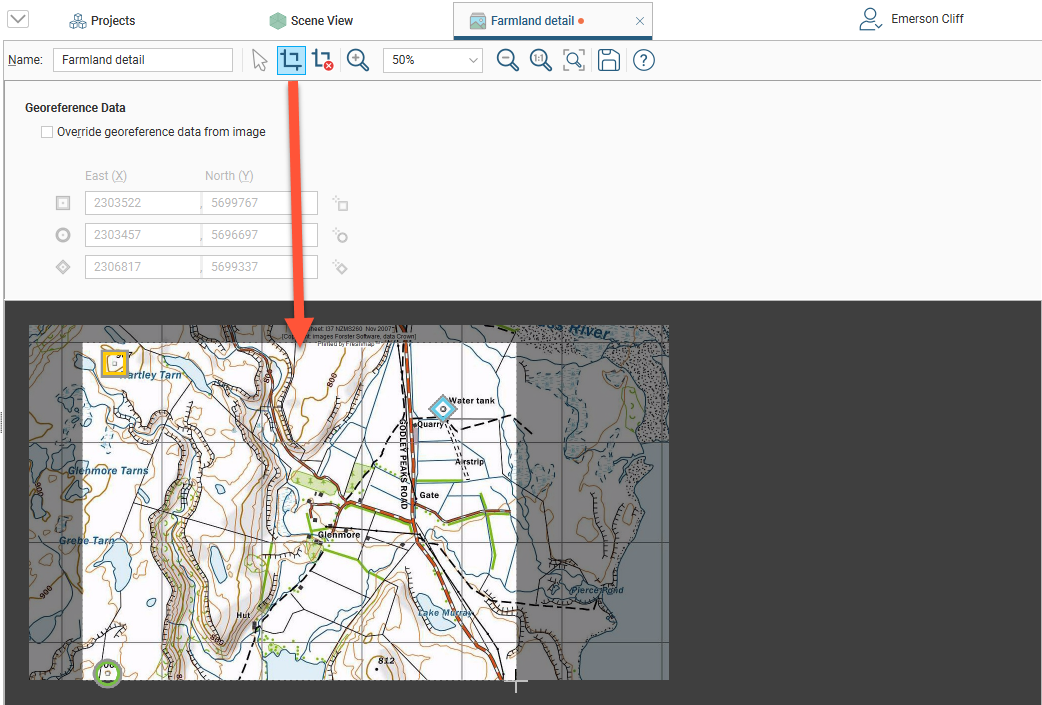
Click on the Remove Crop button (![]() ) to clear the cropping.
) to clear the cropping.
Exporting a Georeferenced Image
Leapfrog Works exports georeferenced images as GeoTIFFs. To do this, right-click on it in the project tree and select Export. You will be prompted for a filename and location. Click Save.
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support
© 2022 Bentley Systems, Incorporated