Block Models
The features described in this topic are only available if you have the Contaminants extension.
This topic describes importing block models in Isatis and CSV formats, creating block models in Leapfrog Works, viewing block model statistics and exporting block models. It is divided into:
- Importing a Block Model
- Creating a Block Model
- Displaying a Block Model
- Viewing Block Model Statistics
- Exporting Block Models
Importing a Block Model
Leapfrog Works imports block models in the following formats:
- CSV + Text Header (*.csv, *.csv.txt)
- CSV with Embedded Header (*.csv)
Note that neither CSV format requires a header; once you start the import process, Leapfrog Works will use the data in the file to locate the minimum and maximum centroids. You can view this information and change how the data is mapped before the file is saved into the project.
Block models imported in CSV format must be regular, rotated only about the Z axis. You will also need to map the data in the file to the block model format Leapfrog Works expects.
To import a block model in CSV format, right-click on the Block Models folder and select Import Block Model. Select the file you wish to import and click Open. An import window will be displayed in which you can map the columns in the file to those Leapfrog Works expects. Once you have mapped the required columns, click Next to define the grid.
In the next window, Leapfrog Works uses the data in the file to check the grid definition and confirm that the centroids match. The Values to enter list gives you different options for mapping the data in the file, and you can preview the file data and use it to choose the best option.
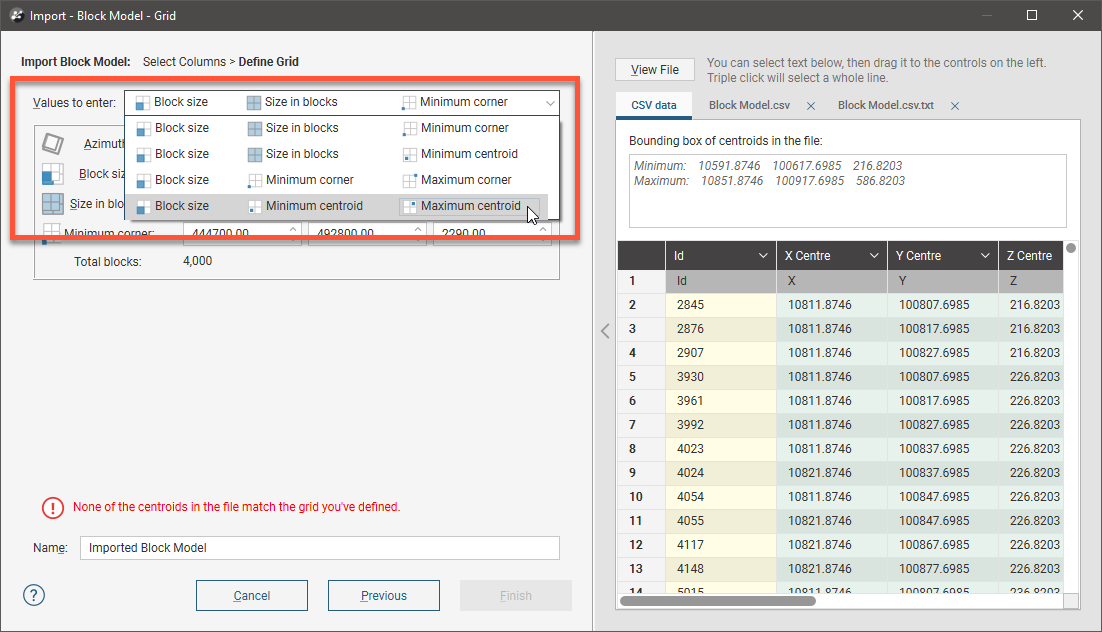
The easiest way to define the blocks is to use the Block size, Minimum centroid, Maximum centroid option. In defining the grid, you can select information in the file and drag it to the corresponding values on the left-hand side:
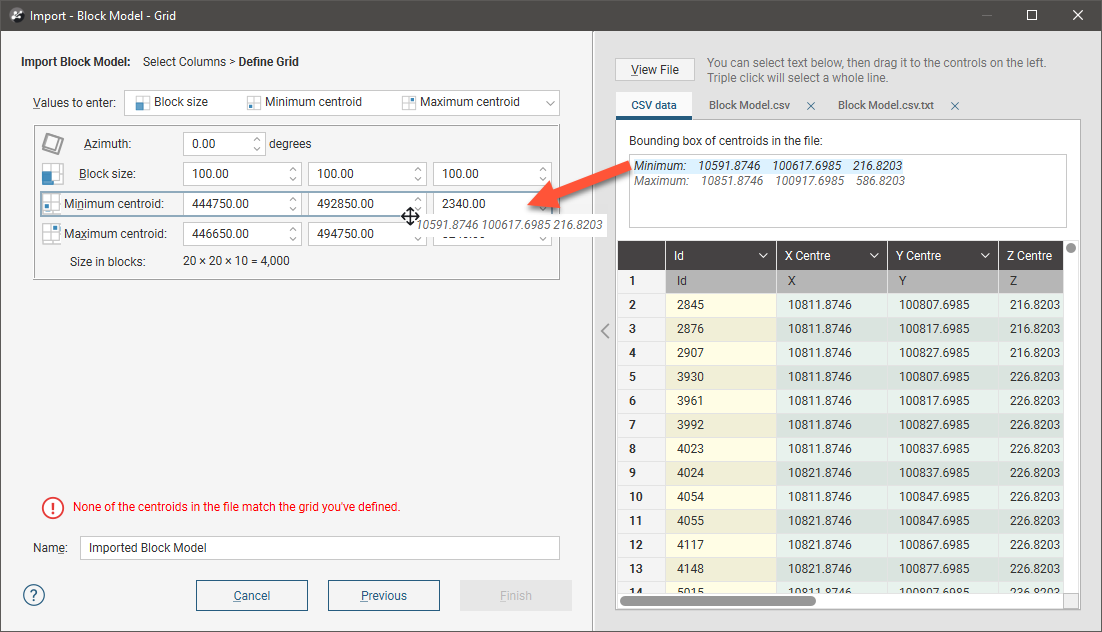
You can also enter the grid definition values manually.
Once the grid has been defined, Leapfrog Works will display a message indicating that the data in the file matches the grid definition:
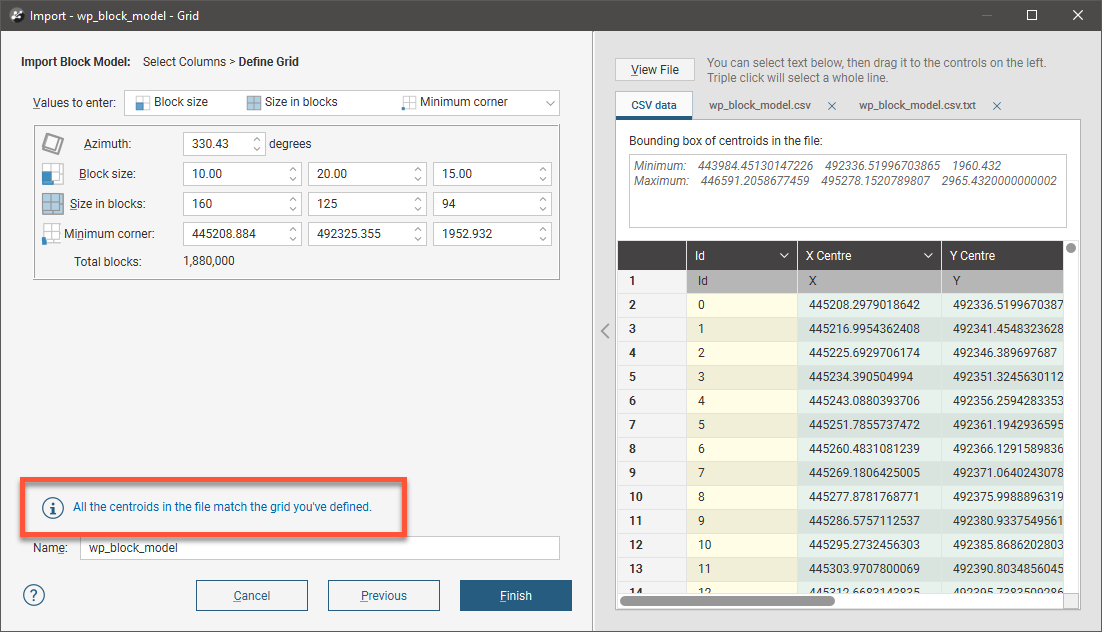
Click Finish. The block model will be imported and will appear in the Block Models folder.
Creating a Block Model
To create a new block model, right-click on the Block Models folder and select New Block Model. The New Block Model window will appear, together with a set of controls that will help you set the size, location and orientation of the model in the scene:
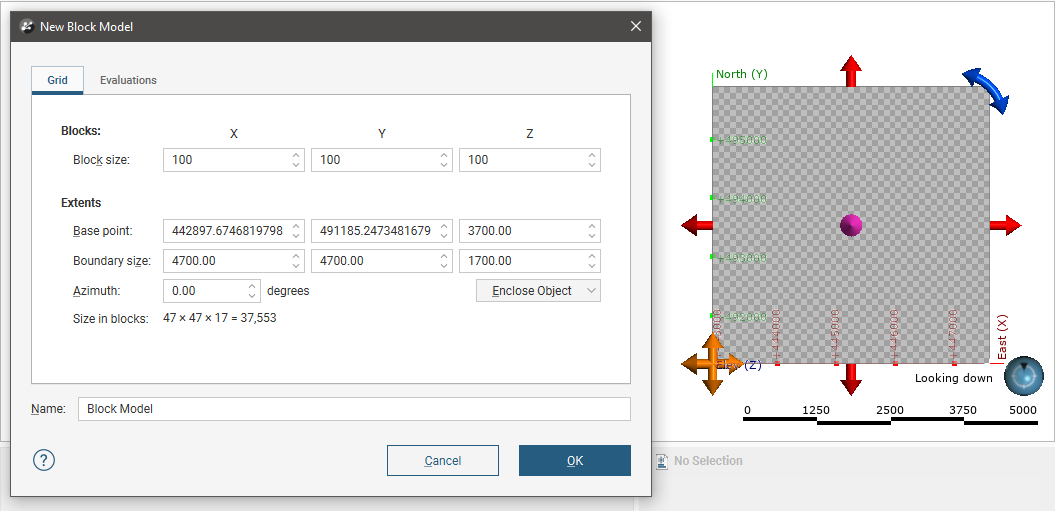
The block model is defined from its Base point, and the reference centroid is the Base point plus one half the Block size. Block models cannot have partial blocks, and when changes are made to the Block size parameter, the model’s extents will be enlarged to match the Block size.
If you know the values you wish to use for the model’s Extents, enter them in New Block Model window. You can also:
- Use the controls in the scene to set the extents.
- The orange handle sets the Base point.
- The red handles adjusts the size of the boundary.
- The blue handle adjusts the Azimuth.
- Use another object’s extents. Select the object from the Enclose Object list.
It is a good idea to use larger values for the Block size as processing time for large models can be considerable. Once you have created a block model, you can change its properties to provide more detail.
You can also evaluate the block model against geological models, interpolants and distance functions in the project. To do this, click on the Evaluations tab. All objects available in the project will be displayed. Move the models you wish to use into the Selected list.
Enter a Name for the block model and click OK. The model will appear under the Block Models folder. You can make changes to it by double-clicking on it.
Displaying a Block Model
When a block model is displayed in the scene, there is an Index Filter option for displaying the grid:
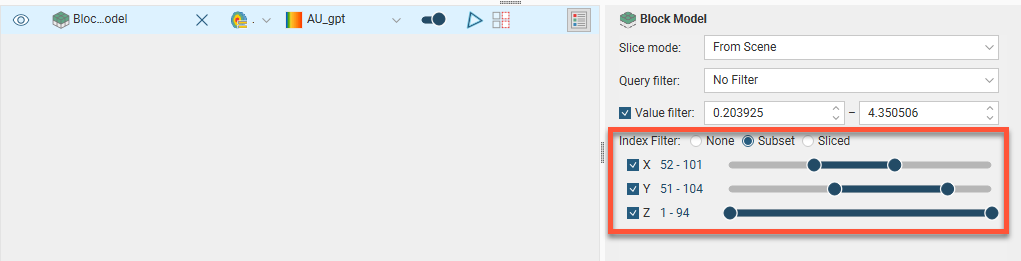
The Index Filter can be set to Subset or Sliced.
- Subset shows the union of the selected X, Y and Z ranges.
- Sliced shows the intersection of the selected X, Y and Z ranges.
The range sliders have two modes: coarse control and fine control. Here an index filter is used for a set of values that ranges from 1 to 160; it is displayed in dark blue, to show the full range of values in coarse control mode:

You can restrict the data displayed by dragging on the handles. Here the range of values is restricted to 1 to 50:

You can click and drag on the selected range to change the values displayed:

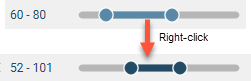
To switch to fine control, double-click anywhere along the range slider. Here the range of 52-101 has been expanded along the whole slider, giving you more control over the position of the range end points:

The slider is displayed in light blue in fine control mode.
Now you can use the handles to further restrict the range displayed:

Right-click on the slider to return to coarse control and the full range of values. Here, right-clicking reverts to coarse control, with the range restricted to the original range of 52-101:
Viewing Block Model Statistics
To view statistics on a block model, right-click on the model in the project tree and select Statistics. The following options are available:
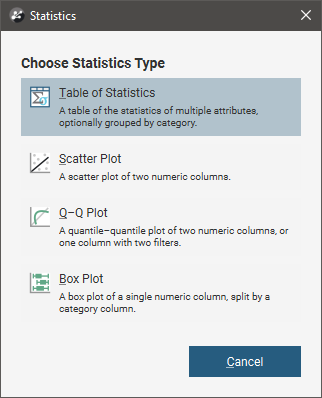
See the Analysing Data topic for more information on each option:
Right-clicking a block model evaluation or a numeric calculation and selecting Statistics opens a univariate graph for the selection. See Univariate Graphs in the Analysing Data topic for more information.
Table of Statistics
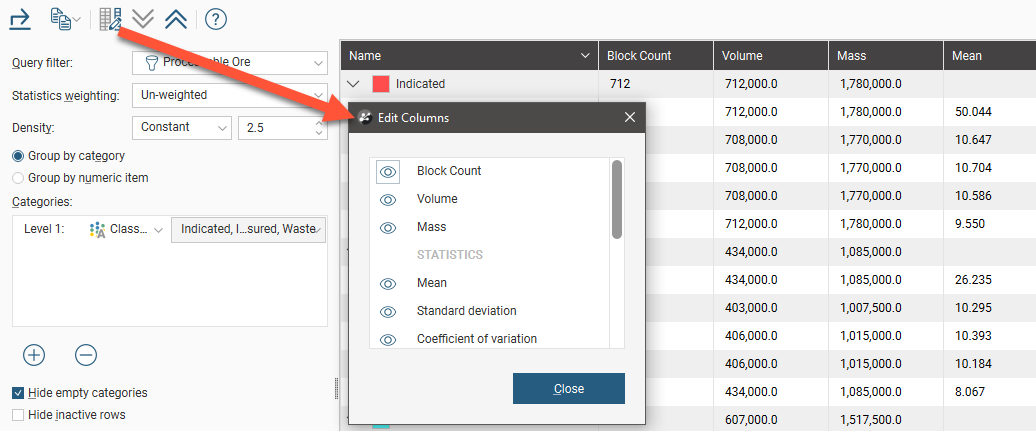
You can view statistics for all evaluations and calculations made on a block model broken down into categories and organised by numeric evaluations and calculations. To view statistics, right-click on a block model in the project tree, select Statistics then select the Table of Statistics option.
You can view statistics for as many numeric and category columns as you wish. When you have at least one Category column selected, you can organise the information displayed in two ways: Group by Category or Group by Numeric. Here, statistics are displayed organised by the category data columns:
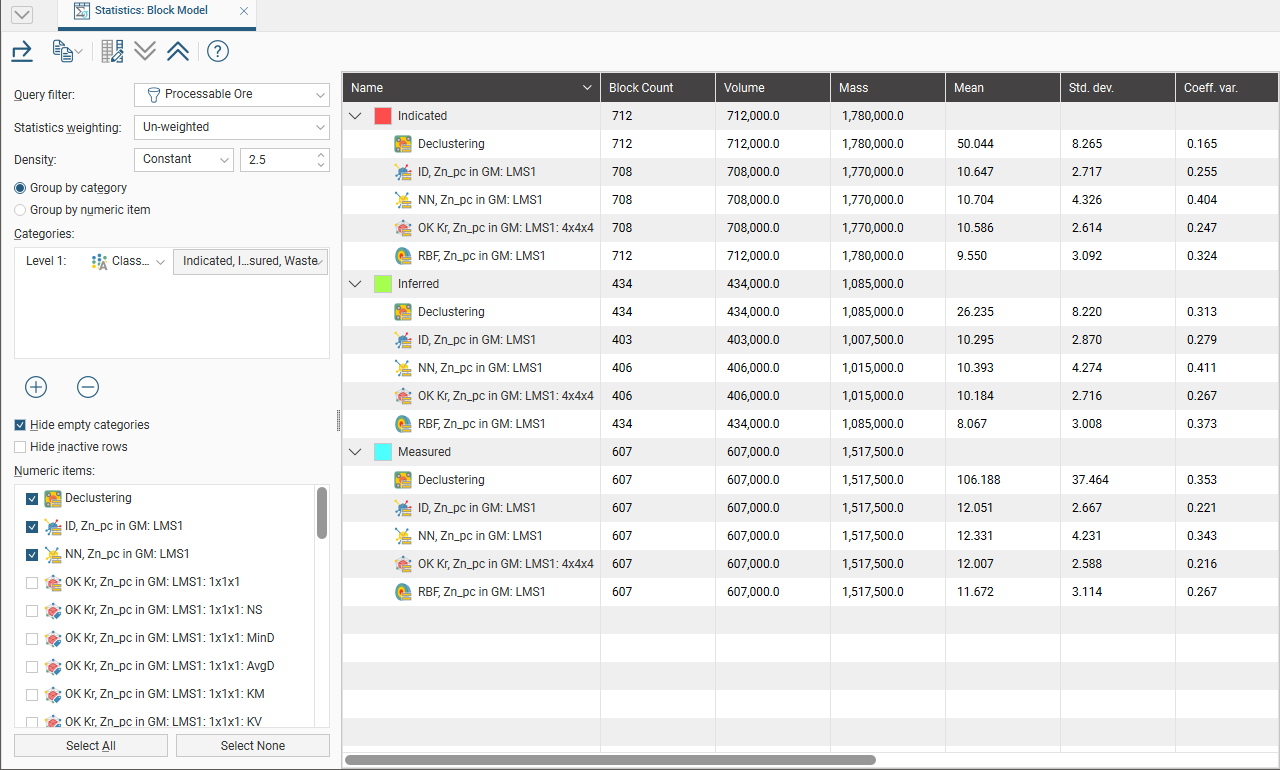
The Query filter option uses a related filter to constrain the data set to a selected subset.
Statistics can be unweighted, weighted by volume or weighted by tonnage. Select the option you require from the Statistics weighting list.
You can also set the Density to be a Constant value that you specify, or you can use the one of the columns in the table.
The Categories list provides category classification options. When selected, the set of statistics measures for each evaluation or numeric calculation will be shown for each category.
You can hide empty categories (those with a count of zero) and inactive rows using the options below the Categories list:
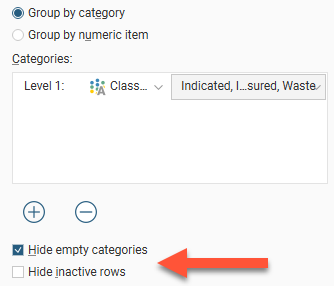
Group by category and Group by numeric column provide options for the table organisation. You can also change what columns are displayed in the table by clicking the Edit columns button (![]() ). This opens a window in which you can select the columns that are displayed in the table:
). This opens a window in which you can select the columns that are displayed in the table:
Click rows to select them, and select multiple rows by holding down the Shift or Ctrl key while clicking rows. You can then copy rows by clicking the Copy button (![]() ), which allows you to copy the selected row(s) or all rows in the table.
), which allows you to copy the selected row(s) or all rows in the table.
The arrow buttons quickly expand (![]() ) or collapse (
) or collapse (![]() ) rows.
) rows.
Exporting Block Models
Block models created in Leapfrog Works can be exported in the following formats:
- CSV + Text Header (*.csv, *.csv.txt)
- CSV with Embedded Header (*.csv)
- CSV as points (*.csv)
To export a block model, right-click on the block model in the project tree and select Export. You will be prompted to select the file format.
Enter a name and location for the file and click Save. Next, you will be able to choose custom settings for the selected format.
The selections you make when you export a block model will be saved. This streamlines the process of subsequent exports of the model.
When you choose to export a block model in CSV format, you must first choose the type of CSV export. Options are:
- With an embedded header file. The block model definition is included at the top of the CSV file.
- With a separate text header. The block model definition is written as a separate text file.
- As points. The CSV file does not include the block sizes and model description.
Click Next. The steps that follow are:
- Selecting From Evaluated Items
- Setting Row Filtering Options
- Setting Numeric Precision
- Setting Status Code Text Sequences
- Selecting the Character Set
Selecting From Evaluated Items
Choose which objects will be included in the exported file. The Available items list includes all evaluations made onto the model. The order of columns in the exported file will match the order shown in the project tree.
Click Next.
Setting Row Filtering Options
You can use a Query filter to filter rows out of the data exported.
This is different from exporting filters as columns, as selected in the previous step.
The second option in this window is useful when all block results are consistently the same non-Normal status. Select from Error, Without value, Blank or Outside; all rows that consistently show the selected statuses will not be included in the exported file.
Click Next.
Setting Numeric Precision
There are three encoding options for Numeric Precision:
- The Double, floating point option provides precision of 15 to 17 significant decimal places.
- The Single, floating point option provides precision of 6 to 9 significant decimal places.
- The Custom option lets you set a specific number of decimal places.
To change either the Centroid and size precision and Column data precision options, untick the box for Use default precision and select the required option.
Click Next.
Setting Status Code Text Sequences
When a block model is exported, non-Normal status codes can be represented in the exported file using custom text sequences.
The Status Code sequences are used for category status codes and filter status codes exported as columns. For filter status codes, Boolean value results will show FALSE and TRUE for Normal values or the defined Status Codes for non-Normal values.
Numeric Status Codes can be represented using custom text sequences. This is optional; if no separate codes are defined for numeric items, the defined Status Codes will be used.
Click Next.
Selecting the Character Set
The selection you make will depend on the target for your exported file. You can choose a character set and see what changes will be made.
Click Next to view a summary of the selected options, then click Export to save the file.
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support