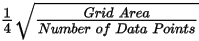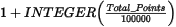Kriging
Use the KRIGRID GX to grid geostatistical data. Kriging determines the most probable value at each grid node based on a statistical analysis of the entire data set.
Kriging dialog options
|
Channel to grid
|
Select the database channel to grid. To specify an array element append to the channel array name the element index in square brackets. The 1st element is element 0.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.CHAN
|
|
Mask channel
|
Select a channel from the drop-down list to act as a mask (or filter) channel. String channels and channels with array size greater than 1 are omitted from the list.
The data values in the channel to grid with corresponding dummy (*) values in the mask channel will not be used in the gridding process.
This field is optional.
Script Parameter: NSI_GRIDDING_CHANNEL
|
|
Output grid
|
Provide the name of the output grid file. The type of file can be controlled using the browse dialog, which is accessible from the [...] button.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.GRID
|
|
Grid cell size
|
Specify a cell size for the output grid. If the cell size is left blank, the default cell size is used. See the Application Notes below for details on calculating the default cell size.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.CS
|
|
Advanced>
|
The advanced options dialog allows you to customize the Kriging parameters. The option to generate only a Variogram without gridding the actual data is found in this dialog.
|
Kriging – Advanced Options
|
Channel to grid
|
(For reference) the selected channel to grid is displayed in non-editable mode.
|
|
Output grid
|
(For reference) the output grid file is displayed in non-editable mode
|
|
Error grid
|
If a file name is provided, the error grid is saved under this name. The error at each grid node is an indication of the degree of confidence. This grid will contain the standard deviation of the Kriging process at each grid node. The resulting output grid will be within 2 standard deviations of the actual value 95% of the time, provided that the selected model (further down) is correct.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.ERR
|
|
Input variogram
|
If a variogram file is entered, it will be used and the variogram calculation will be skipped. If left blank the variogram is calculated according to the model and parameters provided hereafter.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.INVAR
|
|
Output variogram
|
If this is the first time through the variogram calculation or if you have changed the variogram model and/or parameters, provide the name of the file to save the variogram in.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.OUTVAR
|
|
Xmin, Ymin,
Xmax, Ymax
|
X and Y minimum and maximum coordinates. Leaving this entry blank, produces a grid covering the entire dataset. To grid a subset for the data, enter the limits of the bounding rectangle.To default any of these parameters, you must honour their position along the entry by providing the separating commas. Entering a range of ,0,0,0 will cause the grid to cover the maximum limits of the data plus the blanking distance.
If no value is entered for the blanking distance, then the grid will cover the maximum limits of the data plus 8 times the grid cell size.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.XY
|
|
Log option
|
You can either grid the original data or its logarithmic (base 10) representation. Gridding the log of the data can be a very effective way to reduce distortion due to highly skewed data such as geochemical data.
The options are:
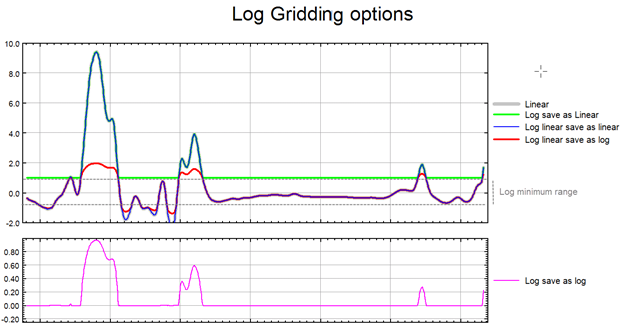
- linear: grid the data as it is.
- log, save as linear: grid the data in logarithmic space and clip all values less than ‘Log minimum’ to the ‘Log minimum’ value, then convert the data back to linear space before saving it to the grid file.
- log-linear, save as linear: grid the data above the positive ‘Log minimum’ and below the negative ‘Log minimum’ in logarithmic space (flip the sign of the data originally in the negative range to take the logarithm then inherit back the sign of the original data; grid the conditioned data). After gridding, all cell values outside the ± ‘Log minimum’ range are converted back to linear space and scaled to maintain continuity at the boundary. Data within the ± ‘Log minimum’ range remains intact and is gridded in a linear sense.
Finally, the linear representation of the data (in both ranges) is saved to the grid file.
- log, save as log: same as ‘log, save as linear’ except that the grid values are kept in log space: the gridded values are saved to the grid file in their logarithmic representation.
- log-linear, save as log: same as ‘log-linear, save as linear’ except that the grid values are not converted back from log space. The output grid is in logarithmic space with the large amplitude anomalies being somewhat moderated.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.LOGOPT
linear: 0 (default)
log, save as linear: -1
log-linear, save as linear: -2
log, save as log: 1
log-linear, save as log: 2
|
|
Log minimum
|
If gridding in log space (see the Log options above), this parameter specifies the minimum value. The default is 1.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.LOGMIN
|
|
Low-pass desampling factor
|
The de-sampling factor is defined as a function of the grid cell size. Before any further calculations, all points within cells of dimension cell_size x desampling_factor are averaged into a single value and placed in the center of the cell.
The default desampling (desampling_factor) is set relative to the contributing points as:
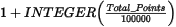
Desampling has two impacts:
If the database contains less than 100000 contributing points, the default is set to 1, and the only pre-filtering consists of de-aliasing at the cell level.
The variogram calculation duration is a function of the square of the contributing points. Increasing this factor visibly cuts down the variogram calculation time while little impact is seen on the variogram curve.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.DSF
|
|
Blanking distance
|
All grid cells farther than the blanking distance from a valid point will be set to dummies in the output grid.
The default blanking distance is calculated as:

Preferably this parameter should be set to just greater than the maximum distance through which interpolation is desired.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.BKD
|
|
Remove trend (drift)
|
If the data manifests a trend, you can remove it from the data prior to gridding.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.RT [Do not remove trend=0 (Default), Remove trend=1]
|
|
Variogram model
|
This selection specifies which of the next 4 parameters are necessary. Options are:
-
User defined (requires input variogram)
-
Power model using power n (n=0 for linear)
-
Spherical model (requires nugget, range and sill)
-
Gaussian model (requires nugget, range and sill)
-
Exponential model (requires nugget, range and sill)
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.MODEL
|
|
Power
|
This is the power for the power model. The default is 1. In this case, the nugget and slope are fit to the data by default if not specified.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.POWER
|
|
Range/Slope
|
Range/Slope. For spherical, Gaussian and exponential models, the range is the distance at which the variogram model reaches the sill value. Beyond the range, the data is uncorrelated. The range must be entered for the spherical, Gaussian and exponential models. For the power model, this is the rate of climb, or slope for a linear model.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.RS
|
|
Nugget
|
The nugget for all models. The nugget is the average error in each data point, and is indicated by the intersection of the variogram model with the h=0 axis. The default is 0.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.NUG
|
|
Sill
|
Sill. This is the level at which the variogram becomes uncorrelated, or goes flat. Beyond the (range, sill) point, the variogram is flat. The sill must be specified for the spherical, power and Gaussian models.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.SILL
|
|
Strike
|
For anisotropic gridding, enter the preferred strike direction angle, measured in degrees clockwise (0°-360°) from the Y axis. This parameter is used in conjunction with the strike weight, below.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.STRIKE
|
|
Strike weight
|
For anisotropic gridding, enter the weighting to be applied to data in the strike direction. The strike weight is the ratio of the semi-major and semi-minor axes of the weighting ellipse, with its major axis oriented in the strike direction. By default, this value is 1 and the medium is presumed to be isotropic.
Script Parameter: KRIGRID.STRIKEWT (Default: 1)
|
|
Variogram Only>
|
Create an output variogram only and do not grid the data. The variogram is automatically plotted and displayed in the "variogram.map".
Note: Any existing map with that name is overwritten.
|
Application Notes
Default Grid Cell Size
The grid cell size (the distance between grid points in the X and Y directions) should normally be ¼ to ½ of the line separation or the nominal data sample interval. If not specified, the data points are assumed to be evenly distributed, and the area rectangular. The default cell size is then defined by the following formula:
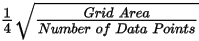
Where:

Log Option
Prior to gridding the data for the 2 log-linear options the data is altered as follows:
if ( Z > Log_minimum)) Z = (log10( Z / Log_minimum) + 1.0) * Log_minimum); if ( 0 < Z ≤ Log_minimum)) Z is untouched if ( -Log_minimum ≤ Z ≤ 0)) Z = -Z if ( Z < -Log_minimum)) Z = -(log10( -Z / Log_minimum) + 1.0) * Log_minimum);
|
Log-linear save as log: The above data is gridded and saved.
Log-linear save as linear: The above data is gridded, All cell values outside the ±Log_minimum range are converted back to linear space and scaled to maintain continuity, then saved.
The illustration below intends to convey the variation between the various log options.
Anisotropic Gridding
In many, if not most, geologic situations, there is a natural bias (anisotropy) of the features of interest in the direction of geologic strike. The strike and strike weight parameters allow you to specify the dominant geologic strike and define preferential weighting in the strike direction. This effectively creates an "ellipse" with the major axis in the direction of strike, and the minor-axis perpendicular to the strike.
The Strike weight (>0.0) is the elliptical weighting (or preference) to apply along strike. The default value of 1.0 creates NO directional bias in the data. Typically, if your data is biased along strike, set the weighting to 2.0. This doubles the importance of data along strike. You can adjust the weighting to achieve a desired outcome by looking at results and experimenting a bit.
A second and related use of these parameters is to correct for anisotropy in the observed sampling pattern. Statistical kriging works best when data is nominally evenly distributed. If you have data collected on lines at a high sample density relative to line separation, you should set the strike direction to be perpendicular to the lines, set the strike weight to be the line separation divided by the along-line sample interval.
KRIG Log Report
Kriging produces a log report of the gridding process. The report gives details about the input data and lists the Kriging parameters. The GX lists the calculated and model variogram, performs the kriging and reports each grid row as it is completed; and finally writes out the output grid and reports the grid parameters.
The Kriging log file contains the following entries:
_______________________________________________________________________
Operating system version
Copyright Information
Gridding Start timestamp
Number of input contributing data points
Number of data points after clustering
KRIGRID Control Parameters:
Grid Cell Size
Grid Origin
Grid Size
Grid Dimensions
Is area clipped ?
Column to grid
Log option
Minimum value for log option
Desampling factor
Blanking Radius
Min/Max Search Radius
Min/Max Search points
Use octant search
Use all data points
Remove trend ?
Variogram model
Variogram power
Variogram model nugget
Variogram model slope
Max. Dist. of Variogram Analysis
Inc. Dist. of Variogram Analysis
Output Grid Specifications:
# points per record
# records
Variogram Analysis:
Model type
Nugget
Slope
Power
Sigma
Variogram_distance_bin Observed_Variogram_value_for_bin Model_Variogram_value_for_bin Number_of_points_in_Bin Bin_Number
.
.
.
Gridding end timestamp
_______________________________________________________________________