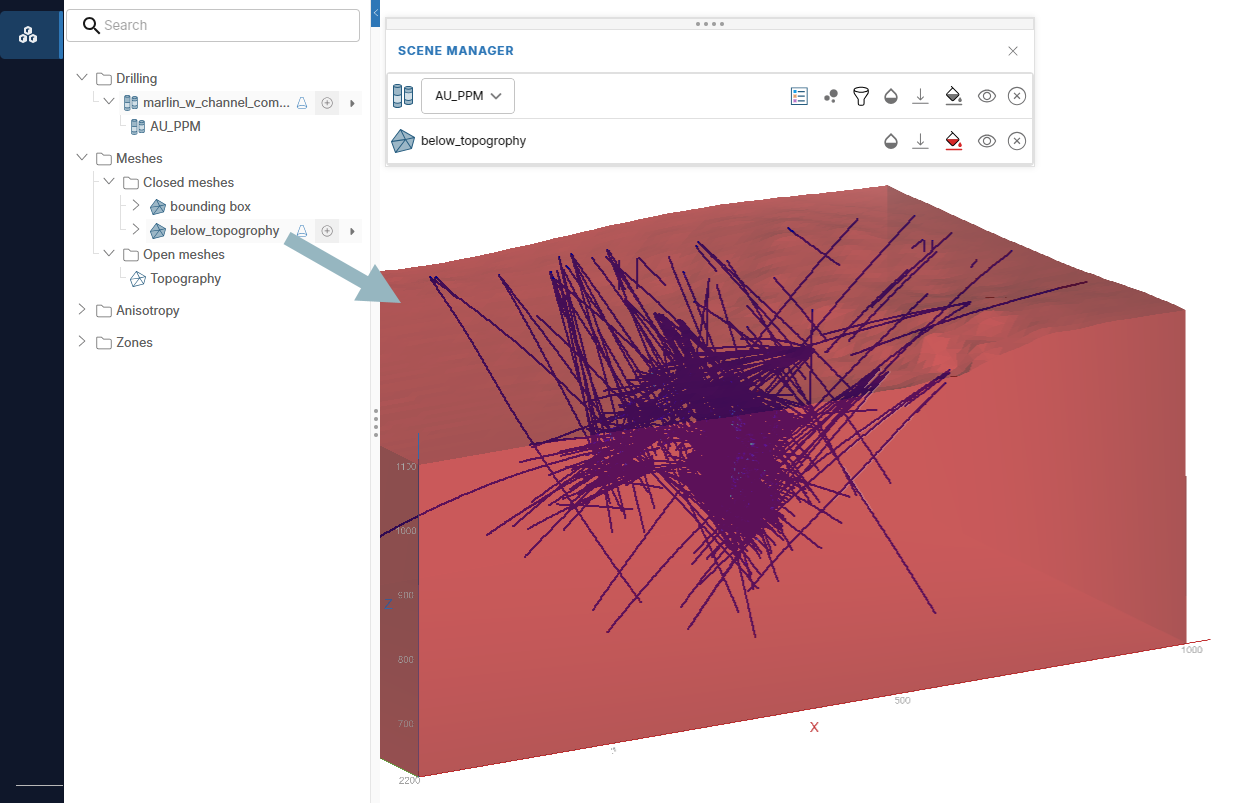
Defining subregions
Driver can use volume and surface meshes to define subregions for the analysis. These are produced as closed and open meshes in the Meshes folder of the project tree.
By default, Driver creates a single closed mesh called a bounding box that encloses all samples in a project. However, you may wish to use your own mesh.
This topic discusses Driver’s tools for defining subregions and recommends strategies for domaining the data in the project. This topic is divided into:
See the Meshes topic for information on importing meshes into a Driver project.
Using meshes as domains
At minimum, Driver requires at least one closed mesh to function, and when drilling data is uploaded for the first time, Driver automatically creates a bounding box and therefore an initial mesh for the project.
Next, refine this subregion by removing the area above the local topography, which can be achieved as described in Clipping a region with a surface later in this topic.
For more complex analyses, the best approach is to start simple and get progressively more complex as required.
- Divide major fault blocks with significant post-mineral/post alteration offset, rotation or lithological changes across the faults.
- Divide any obvious post-mineral intrusive lithologies (e.g. barren rocks) that exhibit hard boundary relationships with the attributes of interest, if that relationship is important to your analysis.
Remember that Driver’s data-driven algorithms recognise and delineate features by incorporating both the elevated and depleted data values. These boundaries may be detrimentally affected or strongly biased by using externally generated interpretive input subregions.
Use the Create mesh from region box tool to divide large datasets down into smaller pieces, which is described below. You can have as many subregions as you like, and it is often easier to organise and structure an analysis by many numerous subregions. Default values, such as SCM tolerance, are set using all samples within each spatial domain.
Be careful not to ‘over-domain’, forcing Driver analysis using pre-existing domain volumes created outside of Driver. While this workflow may be suitable in some cases, such as when using fault blocks, in most cases it is best to begin a Driver analysis with no domains defined. Do not use pre-defined high, medium and low grade geostatistical subregions. Do not divide the analysis into complex lithological subregions. If the geological continuity of various lithological attributes is required, supply this information as a binary (1s and 0s) data attribute column.
Creating a mesh from the region box
You can trim the default bounding box to exclude disparate drilling samples. To do this, right-click on the Closed meshes folder and select Create mesh from region box. In the window that appears, a preview of the region box is displayed, along with controls for adjusting it. Initially, this region box will be scaled to your bounding box size:
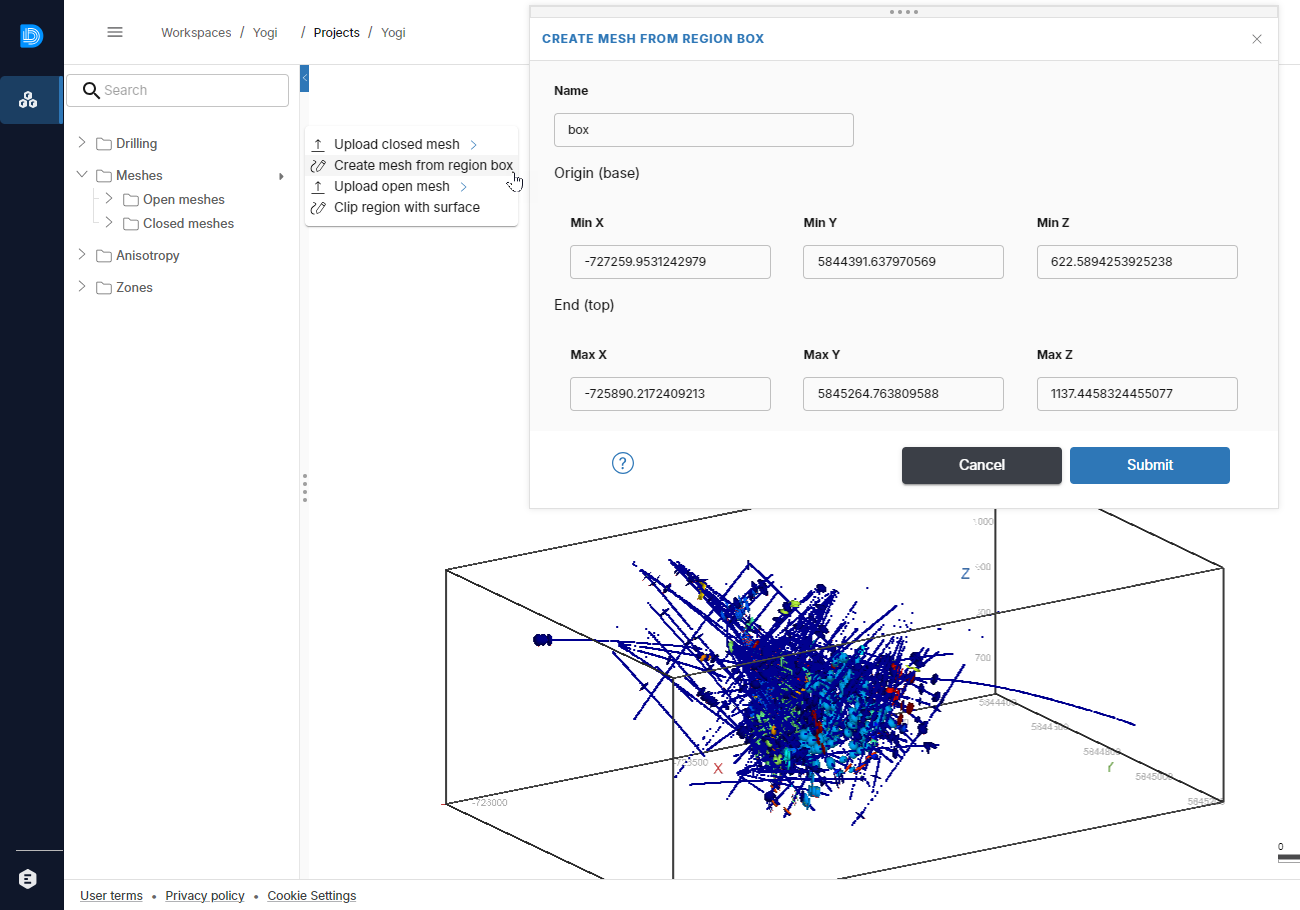
Adjust the limits as required and click Submit.
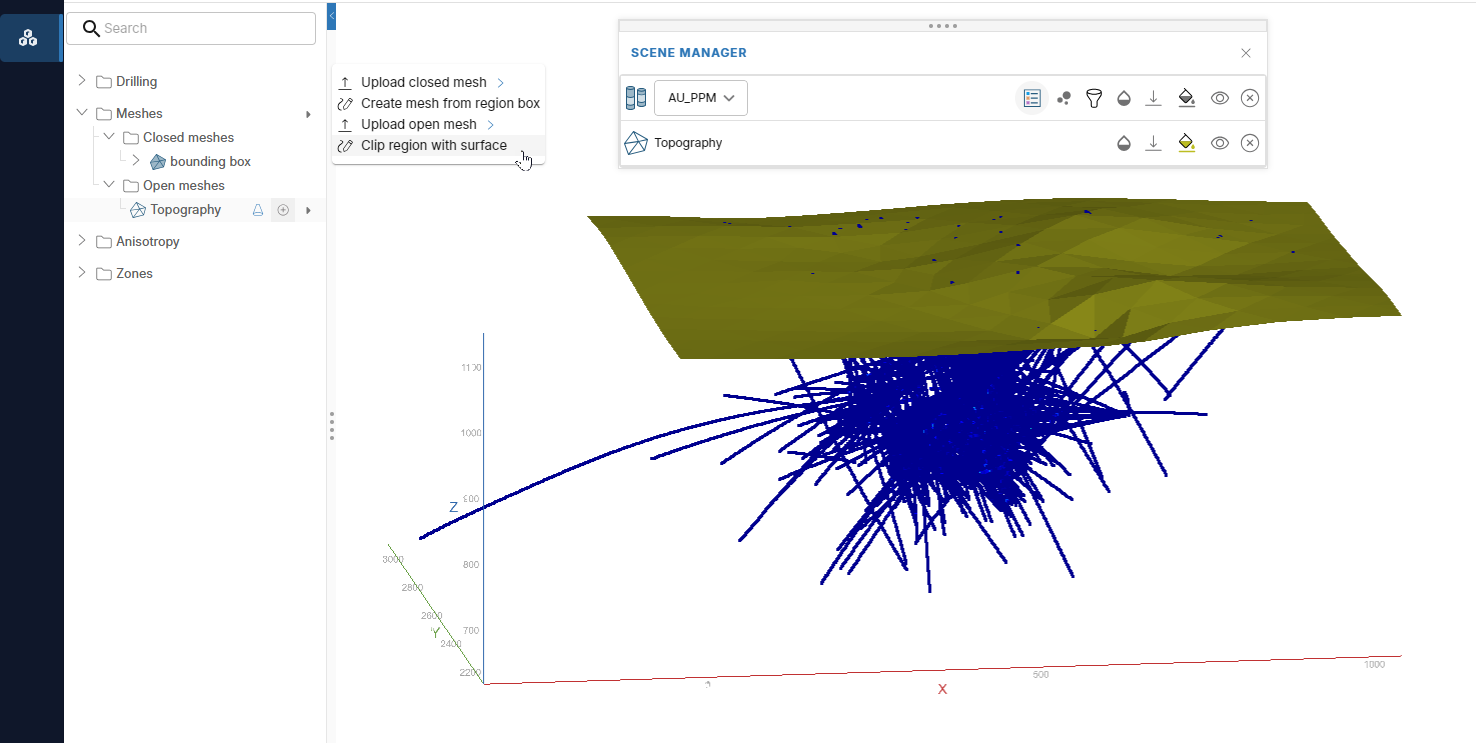
Clipping a region with a surface
To clip a closed region with an open mesh, add the open mesh you wish to use as a clipping surface to the project. Next, right-click on the Meshes folder in the project tree and select Clip region with surface. For example, here we have a topography mesh we will use to clip the project bounding box:
In the window that appears, define the limits of the new region and specify the clipping surface.
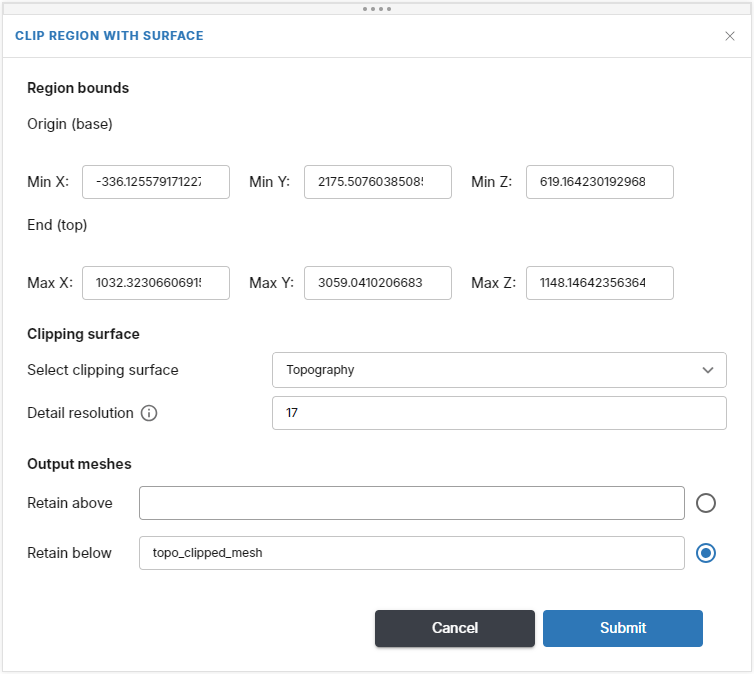
The Detail resolution is the resolution of the clipped surface. The clipped surface will use inverse distance weighted (IDW) estimation to extend the surface to the limits of the region box.
Next, select which part of the surface to keep. In this example the we are clipping the top of the volume with a topography mesh, so the Retain below option has been selected.
Insert an output mesh name and click Submit to create the new mesh, which will be saved in the Meshes > Closed meshes folder.
After the clipping operation is complete, you can add the new object to the scene. For example, here is a closed mesh created by clipping a volume and retaining the volume below the clipping surface: