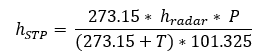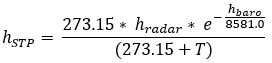Calculate STP Elevation
Use the RPS > Calculate STP Elevation option (geogxnet.dll(Geosoft.GX.Radiometrics.CalculateSTPElevation;Run)*) to apply altimeter correction and calculate the STP equivalent elevation, adjusted for current temperature and pressure conditions. To generate the STP-corrected altitude output, the process requires input from either a barometric elevation or pressure channel, along with temperature and radar altimeter data. For further details, refer to the Application Notes.
To rerun the process with previous settings, select the header cell of any channel created by the process, then right-click to open the context menu. The last item in the menu represents the most recently executed process (GX). Select it to reopen the associated dialog. From there, you can rerun the process with the existing settings, adjust parameters before execution, or simply close the dialog. Learn more about Dynamic Process Links (Makers).
Calculate STP Elevation dialog options
|
Method |
Choose whether to correct the height using standard temperature and either barometric elevation or standard pressure:
Refer to the Application Notes for the correction equations. Script Parameter: SPECTRO.STP_METHOD [0 - Barometric; 1 - Pressure] |
|
Radar altitude channel |
Select the radar altimeter channel. Script Parameter: SPECTRO.RALTRAW |
|
Temperature channel (C) |
Select the temperature channel. Script Parameter: SPECTRO.CTEMP |
|
Barometric channel / |
This is a contextual parameter. Based on your Method selection, either the Barometric channel or the Pressure channel field will be enabled. Script Parameters: SPECTRO.BALTRAW SPECTRO.PRESSURE |
|
Before converting to equivalent height at standard temperature and pressure (STP), you may need to apply light filtering to your radar altimeter data to smooth out abrupt terrain changes.
Script Parameter: SPECTRO.RALTSWAV |
|
|
Output STP altitude channel |
Specify the output channel for the STP-corrected altitude. Default name: RALTSTP Script Parameter: SPECTRO.RALTSTP |
Application Notes
STP Correction Equations
To apply radiometric analysis techniques, actual survey conditions must be converted to standard conditions. This involves adjusting the measured ground clearance to standard temperature and pressure (STP). The resulting "equivalent height" represents the same mass of STP air between the ground and the aircraft as was present during data acquisition.
The STP-corrected altitude can be calculated in two ways, depending on available channels:
Correction for Standard Temperature and Pressure
-
Standard temperature: 273.15 K
-
Standard pressure: 101.325 kPa (equivalent to 101325 Pa or 1 Atm)
To correct the height for standard temperature and pressure, the formula is:
Correction for Standard Temperature and Barometric Elevation
The calculation above assumes the availability of radar altimeter, temperature, and air pressure data. However, some systems may not provide direct pressure measurements. In such cases, barometric altimeter readings can be used.
To correct the height for standard temperature and barometric elevation, the formula is:
Where:
hradar - Observed height above ground level (metres)
hbaro - Barometric height above sea level (metres)
hSTP - Equivalent height at STP (metres)
T - Air temperature (°C)
P - Barometric pressure (kPa).
Unit Conversions
1 kPa = 10 mbar
1 Atm = 101.325 kPa
Processing Workflow
This RPS tool performs two processes:
-
Low-pass filtering of radar altimeter data
-
STP correction of altitude
After processing:
-
If results are unsatisfactory, rerun the GX and adjust parameters as needed.
*GX.NET tools are embedded in the geogxnet.dll file located in the \Geosoft\Desktop Applications\bin folder. To run this GX interactively (outside the menu), first navigate to the bin directory and provide the GX.NET tool in the required format. See the Run GX topic for more guidance.
References
- [1] G. Erdi-Krausz et al. (2003), Guidelines for Radioelement Mapping Using Gamma Ray Spectrometry Data, IAEA-TECDOC-1363, International Atomic Energy Agency.
https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/te_1363_web.pdf - [2] IAEA (1991), Airborne Gamma Ray Spectrometer Surveying, Technical Reports Series No. 323, International Atomic Energy Agency.
https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/22/072/22072114.pdf
Got a question? Visit the Seequent forums or Seequent support
Copyright (c) 2025 Bentley Systems, Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Privacy | Terms of Use